Understanding the Differences between HCI and 3 Tier
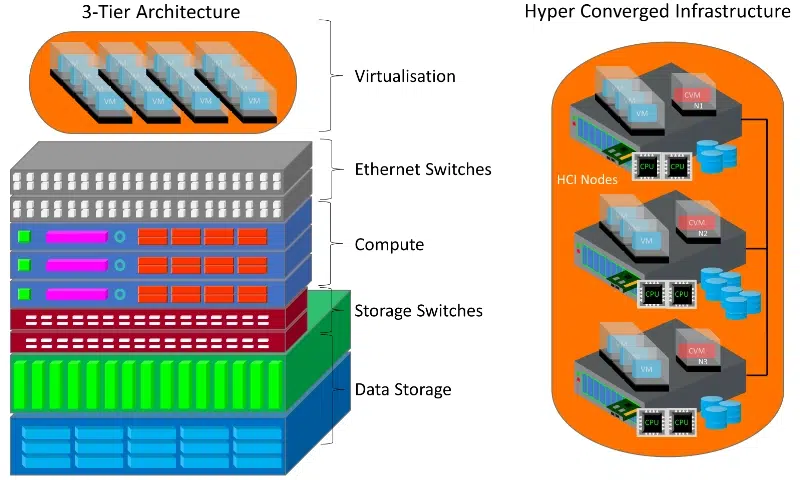
HCI and 3 Tier architecture serve different purposes in the IT landscape. HCI, or Hyper-Converged Infrastructure, combines computing, storage, and networking into a single solution. This integration simplifies management and enhances scalability.
On the other hand, 3 Tier architecture divides applications into three distinct layers: presentation, application logic, and data storage. Each layer can be managed independently. This separation allows for flexibility in development but can complicate deployment.
When it comes to performance, HCI often delivers speed due to its unified approach. In contrast, the layered structure of 3 Tier might introduce latency as requests move between tiers.
Cost is another differentiator. HCI may require higher initial investment but could lead to lower operational costs over time through efficient resource utilisation. Meanwhile, traditional 3 Tier setups allow businesses to scale incrementally according to their needs without significant upfront expenditures.
Advantages of HCI over 3 Tier Architecture
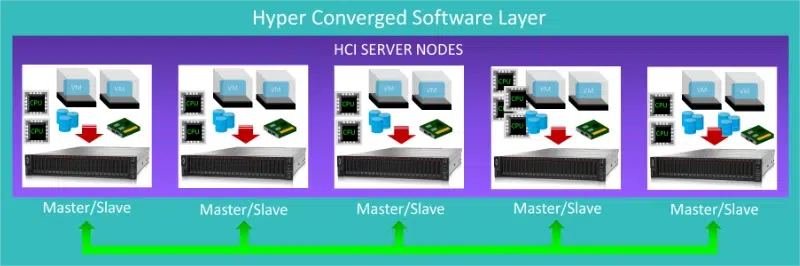
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) offers a streamlined approach to IT management. One of its primary advantages is simplicity. By integrating storage, computing, and networking into a single system, HCI reduces complexity significantly.
Scalability is another key benefit. With HCI, businesses can easily add nodes as their needs grow without overhauling existing infrastructure. This flexibility allows for more efficient resource allocation.
Cost-effectiveness also stands out in HCI solutions. Organisations can save on hardware expenses by minimising the need for separate components typically required in traditional 3 tier setups.
Moreover, HCI often features built-in data protection mechanisms that enhance security and compliance measures right out of the box. This integration simplifies backup processes compared to managing separate systems in a 3 tier architecture.
Deployment speeds are faster with HCI due to its unified platform nature; this means quicker time-to-market for new applications or services.
Advantages of 3 Tier Architecture over HCI
3 Tier Architecture offers distinct advantages that can cater to specific business needs. Its structured approach separates the presentation, application, and data layers. This separation allows for more flexibility in development and deployment.
Scalability is another strong point. Each layer can be scaled independently based on demand. If your user base grows, you can enhance just the presentation layer without overhauling the entire system.
Maintenance becomes easier too. With clear boundaries between layers, troubleshooting problems or upgrading components is straightforward. Developers can focus on enhancing one part without affecting others.
Additionally, 3 Tier systems often leverage existing hardware efficiently through a hypervisor setup. This means businesses may not need to invest heavily in new infrastructure immediately while still enjoying enhanced performance.
Security also benefits from this architecture as each tier can enforce its security protocols tailored for specific functionalities or data sensitivity levels.
Choosing the Right System for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right system for your business involves a careful analysis of specific needs. Start by identifying your workloads and applications. Are they resource-intensive, or do they require flexibility?
Consider scalability as well. HCI systems usually offer robust scaling options due to their integrated nature. This is crucial if you anticipate growth.
Evaluate costs too—both initial investment and long-term maintenance. A 3 tier architecture may have lower upfront costs but could incur higher operational expenses over time.
Think about management complexity as well. HCI tends to simplify management through centralised control, while a 3 tier setup might necessitate specialised skills for each layer.
Don’t forget about vendor support and community resources. Strong backing can help ease transitions and troubleshooting down the road. Tailoring these factors to fit your unique situation will enhance productivity and efficiency in the long run.
Conclusion
When it comes to selecting between HCI and 3 Tier architecture, the decision largely hinges on your specific business needs. Hyperconverged infrastructure offers simplicity, scalability, and efficiency. It’s particularly beneficial for organisations looking to streamline operations with minimal management overhead.
On the other hand, 3 Tier architecture might appeal more to those seeking flexibility in their technology stack. Its modularity allows businesses to customise each layer according to specific requirements or budget constraints.
Understanding both systems' advantages will guide you toward making an informed choice that aligns with your strategic goals. Whether you prioritise ease of use or the ability to finely tune every aspect of your IT environment is key in determining which approach best fits your organisation’s future growth plans.
Summary
At Fortuna Data we provide a range of HCI and 3 tier solutions that can help a business navigate the best way forward to achieve their modernisation, core objectives and goals.